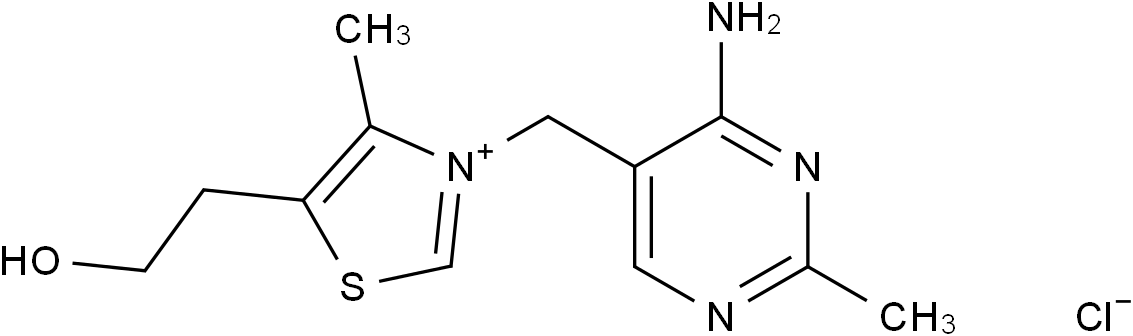
Thiamine monochloride
CAS No. 59-43-8
Thiamine monochloride( —— )
Catalog No. M15204 CAS No. 59-43-8
Thiamine levels in the blood of homozygous KO and KI mice feed a conventional diet are decreased to 0.058±0.051 and 0.126±0.092 μM, respectively.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 37 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | 43 | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameThiamine monochloride
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionThiamine levels in the blood of homozygous KO and KI mice feed a conventional diet are decreased to 0.058±0.051 and 0.126±0.092 μM, respectively.
-
DescriptionThiamine levels in the blood of homozygous KO and KI mice feed a conventional diet are decreased to 0.058±0.051 and 0.126±0.092 μM, respectively, at 7 weeks compared to WT mice (0.796±0.259 μM).
-
In VitroThiamine levels in the blood of homozygous KO and KI mice feed a conventional diet are decreased to 0.058±0.051 and 0.126±0.092 μM, respectively, at 7 weeks compared to WT mice (0.796±0.259 μM). When WT and homozygous KO and KI mice are fed a thiamine-restricted diet (thiamine: 0.60 mg/100 g food), blood thiamine concentration at 5 and 14 days is markedly decreased to 0.010±0.009 and 0.010±0.006 μM, respectively, compared to WT mice (0.609±0.288 μM). Thiamine concentration in brain homogenate of WT mice fed a conventional diet is 3.81±2.18 nmol/g wet weight, and that of KO and KI is 1.33±0.96 and 2.16±1.55 nmol/g wet weight, respectively. Notably, thiamine concentration in brain homogenate decreased steadily in KO and KI mice fed a thiamine-restricted diet (thiamine: 0.60 mg/100 g food) for 5 days (0.95±0.72 nmol/g wet weight) and 14 days (1.11±0.24 nmol/g wet weight), respectively, compared to WT (3.65±1.02 nmol/g wet weight), before the mice presented an phenotype of disease.
-
In VivoWT, homozygous, and heterozygous KO and KI mice feed a conventional diet (thiamine: 1.71 mg/100 g) survive for over 6 months without any phenotype of disease. Homozygous KO and KI mice feed a thiamine-restricted diet (thiamine: 0.60 mg/100 g food) showe paralysis, weight loss, and immobility, and die within 12 and 30 days, respectively. Similarly, homozygous KO and KI mice feed a thiamine-restricted diet with an even lower percentage of thiamine (thiamine: 0.27 mg/100 g food) die within 14 and 18 days, respectively. However, WT and heterozygous KO and KI mice feed a thiamine-restricted diet (thiamine: 0.60 mg or 0.27 mg/100g food) survive for over 6 months without any phenotype of disease.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research AreaOther Indications
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number59-43-8
-
Formula Weight300.81
-
Molecular FormulaC12H17ClN4OS
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityN/A
-
SMILESCC1=C(CCO)SC=[N+]1CC2=CN=C(C)N=C2N.[Cl-]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Kenneth Osiezagha, et al.Thiamine Deficiency and Delirium. Innov Clin Neurosci. 2013 Apr; 10(4): 26-32.
2. Kaoru Suzuki, et al. High-dose thiamine prevents brain lesions and prolongs survival ofSlc19a3-deficient mice. PLoS One. 2017; 12(6): e0180279.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Vazegepant HCl
Vazegepant is the first intranasal gepant for the acute treatment of migraine and has announced a positive phase II/III study.
-
SDV-Exendin-3/4
SDV-Exendin-3/4 is a 32-amino acid peptide.
-
Angiotensin 1/2 (1-9...
Angiotensin 1/2 (1-9)TFA is containing the amino acids 1-9 that are converted from Angiotensin I/II peptide.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


